|
|
||
 |
Respiration |
|
|
|
||
Contents: |
|
|
||||||||
Definition:
Respiration is the process in which the body breaks down molecules to release energy. Respiration occurs on two levels: cellular and organism levels. On a cellular level, energy from glucose molecules is converted into energy in ATP molecules. The body can use the energy in ATP to carry out life processes. Respiration on an organism level is the gas exchange between the organism and the environment. (Respiration isn�t breathing. Breathing is respiration on an organism level)
Cellular Respiration- A cell needs energy from ATP molecules to carry out life processes. Cellular respiration is the process in which the cell uses ATP to get energy.
ATP is an abbreviation for Adenosine Tri-Phosphate.
A � P ~ P ~ P
The A is the Adenosine and the P is a phosphate group. ATP is a nucleic acid. The squiggly lines are high-energy bonds. When these bonds are broken, energy is released and this is what the body uses to carry out life processes. The high-energy bonds are broken with an enzyme called ATP-ase.
When ATP molecules are broken down, they release energy. The result of the reaction is ADP or Adenosine Di-Phosphate (One phosphate group is released as a result from the reaction. Now there is only two.) The cell then changes the ADP molecules back into ATP by adding another phosphate group. However, this reaction needs energy to take place. Energy from the breakdown of Glucose and other simple sugars are used to power this reaction. The body uses energy from glucose to produce ATP, and then breaks down ATP to release energy that the cell uses.
How does the body get energy from glucose? There are two different ways. One is anaerobic (without oxygen), and the other is aerobic (with oxygen). Humans use aerobic respiration on a regular basis.
1. Anaerobic Respiration � another name for anaerobic respiration is Fermentation.
With different enzymes, the body breaks down Glucose into Pyruvic Acid. As a result of the reaction, enough energy is released to complete the ATP-ADP cycle four times. However, 2 ATP are needed to power this reaction. The net gain of this reaction is 2 ATP. Net gain is the overall outcome of energy gained as a result of the reaction. It is calculated by subtracting the activation energy from the energy released from the reaction. (4-2=2) Activation energy is the Energy needed in order for the reaction to take place. The Pyruvic acid is broken down in to Lactic acid in animal cells, and Ethyl alcohol in plant cells. These are waste products and are excreted from the cells.
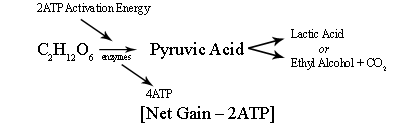
Humans can carry out anaerobic respiration on a temporary basis. When the cells are cut off from oxygen (Oxygen Debt), they use anaerobic respiration, and produce lactic acid. Lactic acid cannot be excreted from the cell and accumulates especially in muscle cells. This causes muscle fatigue. When oxygen is restored to the cells, the lactic acid is changed back into pyruvic acid.
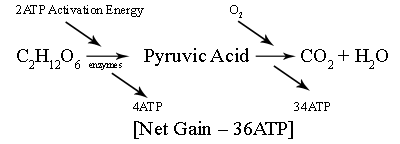
The first part of Aerobic respiration is the same as anaerobic respiration. 2ATP is used to break down Glucose into pyruvic acid resulting in 4ATPs worth of energy. This part is call the anaerobic phase. Then, with oxygen, pyruvic acid is broken down into H2O and CO2, which are the wastes. As a result of this reaction, 34ATPs worth of energy is produced. This is much more efficient than anaerobic respiration because the net gain is 36, 18x more than anaerobic.

Return to Freshman Review Sheets
Review Sheets Central 2001
www.reviewsheetscentral.com