|
|
||
 |
Plant Maintenace |
|
|
|
||
Contents: |
|
|
||||||||
Plants are autotrophic and make their own food. The plants produce the food in the chloroplasts through photosynthesis. The plant produces food from Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Water (H2O). In the presence of chlorophyll, light, and enzymes, the plant produces glucose, oxygen, and water. Here is the equation.
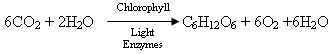
The Carbon Dioxide and the water are raw materials; the Chlorophyll, water, and enzymes are catalysts; the glucose is used to produce energy; and the Oxygen and Water are wastes.
Plants get the water from the soil through the roots. On the roots are microscopic hairs that absorb water as well as other minerals from the soil. There are root hairs to increase the surface area and therefore be able to absorb more water.
Plants get the Carbon Dioxide from the air through stomates. Stomates are microscopic holes on the bottom of a leaf in which the Carbon Dioxide enters the leaf. They are also used to release Oxygen and Water vapor from the plant. The stomates are surrounded by two guard cells, which expand and contract. When they contract, the stomates grow bigger, and let more water go out of the leaf. They expand when there is an excess amount of water. When there is a drought, the stomates grow smaller to conserve water. This is a homeostatic mechanism.
Wavelengths of Light- light are really made up of different colors of the rainbow. Different colors are absorbed by the plant better than others. Blue and red are absorbed the best, while green is absorbed the least.
Photosynthesis is carried out in two stages: Photolysis (light reaction) and Carbon Fixation (dark reaction). The first part can only take place in the presence of light, while the other can be produced even in the dark.
1. Photolysis- In photolysis, the light activates electrons in the chlorophyll molecule and these electrons split the water molecule. The Oxygen is released into the air as a waste. This is the oxygen we use to breathe. The hydrogen is transported to the next part of the reaction by a carrier molecule (TPN).
2. Carbon Fixation- The hydrogen from photolysis is combined with Carbon dioxide to produce glucose. The first molecule in the process is PGAL. H2O is a waste.
Glucose is then transported to the mitochondria where, through aerobic respiration, it is used to produce ATP.
Lenticels- Structures found in the green stems and are used for gas exchange. They have the same purpose as the stomates, but they have no guard cells.
Vascular tissue is the piping of the plants. It is how the plant transports substances from one part to another. There are two tubes in the plant called the Xylem and Phloem. The xylem is dead cells and they transport water and minerals from the roots, to the stems and leaves. The phloem is living tissue that carries glucose and other nutrients up and down the plant.
Transpiration is the theory of how the plant manages to get water up the plant through dead cells. It says that water, evaporating out of the stomates, drags up water behind it.
Regulation is the reaction of the plant to a stimulus that results in growth or movement. That means that a plant reacts a certain way to different things in the environment and grows in a certain way because of it. Not all parts of a plant grow equally. The response is described as either a positive or negative tropism (tropism- response).
- tropism = growth away from the stimulus
+ tropism = growth towards the stimulus
| Stimulus | Name | Tropism | |
| Stems & Leaves | Roots | ||
| Light | Phototropism | - | + |
| Water | Hydrotropism | + | - |
| Gravity | Geotropism | + | - |
Auxins are hormones that regulate the growth of the plant. They are responsible for tropisms. They cause growth that is uneven. By going to one side of a stem, it causes it to grow longer causing the stem to bend the opposite way. Auxins are produced in root and stem tips and are distributed throughout the phloem.
Cambium is special group of cells in the stems, which are responsible for lateral growth (width, side to side). Maristem is special group of cells in the stems, which are responsible for vertical growth (stimulated by auxins). It is found on the tips of stems and roots.
Growth of a plant varies with the seasons. In the fall, temperature gets colder, and days get shorter. Auxins migrate from the nodes in the leaves where they are produced, resulting in the formation of Abscission cells at the node. Abscission cells interrupt the Xylem and Phloem from the leaf. The leaf is cut off from water and minerals, and the leaf dies. They also waken the connection between the leaf and the branch, causing the leaf to fall off.
Dormancy is the plant equivalency of hibernation. Everything in the plant slows down and even temporarily stops. This is a defense mechanism because if they don�t loose their leaves, they would die.
The leaf is made up of different parts. If you take a cross-section, on top would be a waxy layer. This is a homeostatic mechanism that helps prevent evaporation of the water through the leaf. Under the waxy layer is a layer of Palisade cells. They absorb sunlight and are the main sight of photosynthesis. Under the palisade cells, is a spongy layer, which acts as a reservoir. Water is stored there with other minerals. There are also cells randomly arranged in there. On the bottom of the leaf are the stomates, as well as a thin spongy layer. The CO2 absorbed by the stomates are dissolved into the spongy layer.

Return to Freshman Review Sheets
Review Sheets Central 2001
www.reviewsheetscentral.com