|
|
||||||||
|
||||||||||
History of Forensics (people)
Forensic science = criminalistics
1- Sir Arthur Canon Doyle- Author of Sherlock Holmes books- he was the first man to inspire the study of Forensic science.
2- Mathieu Orfillia- father of forensic toxicology- studied poisons in animals and how to detect the poisons.
3- Alfonse Bertillon- father of forensic identification- devised the first plan of how to identify suspects and for the police to keep track of the people
-Method = anthropometry.
4- Francis Galton- devsed second method for identification = finger prints (he also wrote a text book called �finger prints�
5- Leone Lattes- discovered how to use dry blood stains and grouped them into blood types (A, B, AB, O)
6- Calvin Goddard- incorporated the comparison microscope into the use of firearm examination
7- Albert Osborn- did documentation examination
-Used documents found as evidence (found- forgeries, used it as blackmail, or documents used to embezzle money)
8-Walter C McCrone- introduced microscopes to the study of forensic science.
9-Hans Gross- made forensic science a form of science.
10-Edmond Locard- �Exchange principle�
-stated that when someone goes to a crime scene they usually leave something of their at the crime scene and pick something up from tehj crime scene (unknowingly)
1923-
1- First crime lad made in Los Angelos.
-August Vollmer- he made the first crime lab in LA
-The lab did not have an official status.
1932-
2-J Edgar Hoover- Director of the FBI
- Created the largest crime lab in US (it was an official crime lab)
1972-
3-California department of justice-
-Created a network of forensic labs
-Britain made a national system of regional labs (everything was controlled by the government)
Increase in Crime Labs due to:
1-increase in crime rates
2-increase in drug crimes
3- the court passed many rules that said you are unable to have a confession alone anymore- you must have evidence to back it up.
4-also they were coming out with new technology such as DNA
4 fields
1-Anthropologist- study of the body
2-Entomologist- study of insects
3-Odontologist- study of teeth
4-Physiciatry- study of human behaviors.
Forensic Units (9 units)
1- Biology Unit-
-DNA
-Hair
-Fiber
-Botanical (plants)
2- Firearms unit
-Study of guns and bullets
-Cartridges
-shot gun shells
-residues-(powders)
3-Physical Science-
-drugs
-glass
-paint
-soil
-explosives
4-toxicology-
-body fluid examination
5-documentation-
-hand writing
-font
-ink
-paper
6-photogrophy-
-taking pictures
7-voice print analysis-
-detects if you are using a fake voice
8-polygraph-
-lie detecotor
Crime scene-
1- police arrival
2- evacuate all the people
3- arrest the suspects
4- close off scene and set the boundaries.
Prime investigator �
1-is appointed by police captain and he appoints other people to do other jobs for him.
He is responsible for:
1-determines the boundaries
2-walk through
3-assigns other people tasks
What is a walk through?
1-looks for evidence
2-the crime lab has evidence collection technicians that know what type of things you are looking for when you are looking for evidence.
***Especially looking for point of entry and point of exit.
3- Interview witnesses.
Recording information:
1-photogrophy- first you take pictures from the place where you can get a picture of the entire room (area) and then you take close ups (this way you can see the objects in relation to other things in the area and then you can see details on the object) (for example the best place to get the best picture of the entire room would be to stand n the corner.)
2-notes- the investigator will take notes so that way if you need to come back to the case a few years later you can have detailed notes on the incident.
Ruff Sketch- diagram of the crime scene (drawn by hand)
1- Need measurements of the scene (length and width of the room/area)
2- Need to measure from the body to the walls
3- Need to measure from the evidence to the walls
4- Need to mark the point of entry and the point of exit.
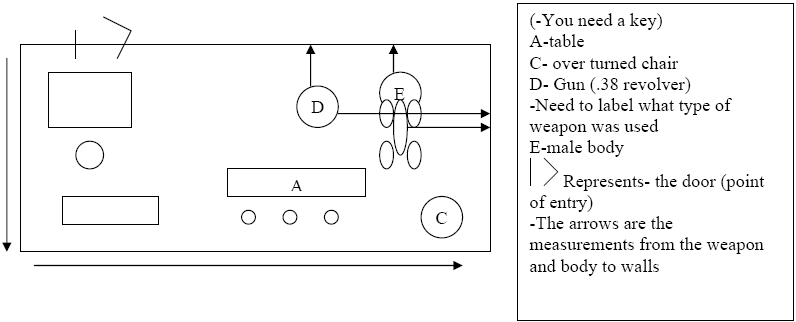
-you also need the person who drew the scene
-the date it was drawn
-the time it was drawn
-the type of murder
-how he was murdered
-measure the length and width of the room
-the address of the place where the murder took place.
When you find a scene you must walk through it in a certain way:
There are 4 ways:
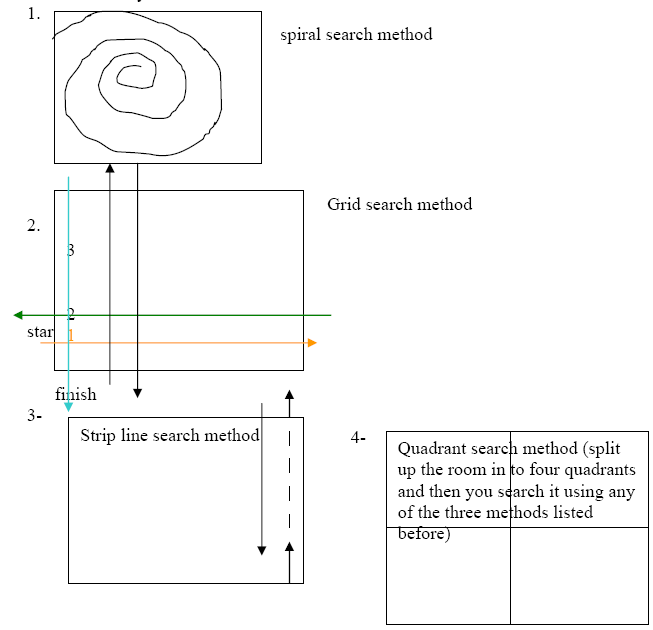
Head investigator takes notes on:
- A detailed description of rime scene
- Identify the physical items found
- Time when items where found
- Name of all individuals they are investigating
- How evidence where packaged after they were photographed
- Who packaged each item
- Where were the evidence sent after packaged.
Safety procedures:
Large contaminated areas:
-You have to wear repellent overalls
Glove and shoe covers
Infectious dust:
Masks
Goggles and face shields
Sharp objects:
Boots/shoes
Thick rubberized clothing
Gloves
Wet blood:
Can�t wear long sleeves b/c if you touch the wet blood you will carry the disease.
Determining the time of Death:
5 catagories of death:
1-homocide
2-suicide
3-accidnet
4-undetermined
5-violent
Rigor Mortis:
The stiffness of the muscles can determine about what time the murder occurred:
-From 24 to 36 hours the muscles start to get tense
After 36 hours the muscles start to relax.
Livor Mortis:
-The blood settles to the side of gravity-
This helps determine in which position you died in, so you can figure out if the victim was moved after they were killed.
(When blood clots it turns purple or blue)
Alcor Mortis-
After death the body temperature drops 1 to 1 � degrees per hour
Until it reaches room temperature
Factors that influence body temperature drop:
1- Location
2- Clothing being worn
3- Body size
4- Weather
K Levels in the eye
K= potassium
Depending on how much potassium is in the eye you can figure out how long the person has been dead for.
Test:
6. skin color becomes blue or purple = livor mortis
7.occurs in the eye fluid = potassium levels
8.is influenced with tight clothing = livor mortis
9. influenced by body size, location, weather = alcor mortis
10.manifests itself within 24 hours and disappears within 36 hours = rigor mortis
11. useful in determining a victims position after death = livor mortis
12.affects the vitreous humor = potassium levels in the eye
13. investigates the cause of a fire or explosions- forensic engineering
14. determine the time of death after murder = forensic entomologist
15.determine the sex, race approximate age of victim after being buried fro 10 years= forensic anthropologist
16. develop the profile of a criminal = forensic psychiatrist
17. analyze the bite marks left on a victim = odontologist
18. reconstruct an accident for a police =engineer
19. conduct insect studies relating to criminal investigation = entomologist
no number 20
21- the number of crime labs in the United States increased because of: supreme court decisions
22-first crime lab in the US to be established: LA
23-the largest crime lab in the US today is in: Washington DC
24- in the US most crime lab resources and time are spent on crimes of: drugs
25- Most smaller municipalities do not have their own crime labs because of: low crime rates, lack of trained personnel, small and inexperienced police department.
26- anthropometry is: the stud of unknown human skeletons
27-the first arriving investigators at a crime should: rope off the area
28- at a crime scene which of the following takes priority over the other choices- secure medical assistance to anyone who needs it
29-it is not the responsibility of a lead investigator to: prepare a finished sketch of a crime scene
30: the main reason for a lead investigator to take notes at a crime scene is: refresh his memory at a later date.
31-40 true and false:
31-police were called coppers because the hats they wore had copper in them: false
32- police where called for assistance by tapping their batons on the floor: true
33- before radios police cars could only receive messages but not broadcasts: true
34-at first police had to hide their funs because they were too threatening or intimidating to the public: true
35-at first the police had to sit in open (convertible�s) cars so that the public could see them: true
36-the �rye standard� refers tot eh standards a witness has to meet in order to be considered an expert: false
37-the decision in Daubert V Merrill Dow Pharmaceuticals requires a judge to accept scientifically accepted concepts: false
38-the temr �gate keeper� refers to a judge: true
39-an expert witness�s testimony must be accepted as fact: false
40-a judge�s flexibility and wide discretion in accepting scientific evidence is exemplified in Coppolino V. State. :true
Evidence- anything that proves that a crime took place
1- direct evidence: = testimonial evidence
ex: when person A says person B was with me on that day so she couldn�t have committed the crime.
2- Physical Evidence: = object or material that is relevant to the crime.
EX: piece of material- gun that was found at the crime scene.
3- indirect evidence: = evidence that does not prove a fact
EX: a shoe print- you can not use a shoe print for evidence but you know that a person was there.
4- Circumstantial Evidence: = implies a fact or event
EX: when a police is driving and sees a car swerving in front of him he thinks that the driver in front of him could be drunk- but he has no proof so it is only circumstantial evidence because the swerving of the car only implies.
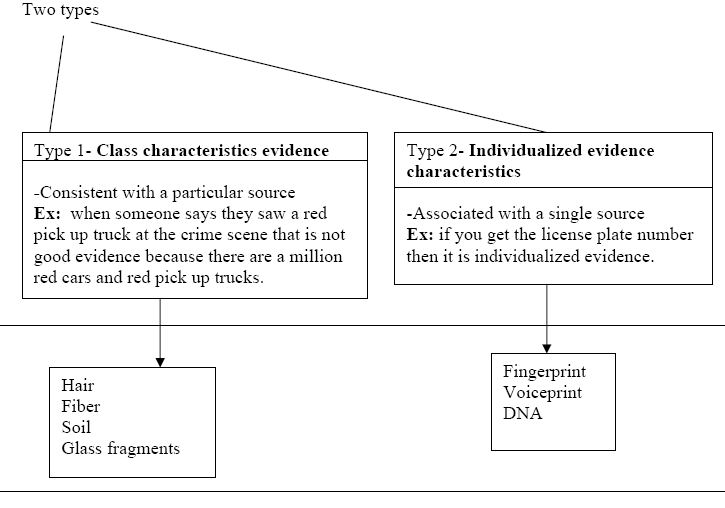
GOOD EVIDENCE- (relevant evidence)
a- Probative evidence: it has to prove something (pro = prove = probative)
b- Material evidence � anything that addresses an issue of the particular crime.
Features to Prove Good Evidence= (things that good evidence must have)
-Has to prove that a crime occurred
-It has to reaffirm that the testimony is true (has to corroborate testimony)
- Link a suspect to the crime scene
EX: DNA links a person to the crime scene because you are able to match up the DNA to the person (suspect)
-Establishes the identity of a suspect
-Evidence has to allow the reconstruction of the crime scene
Admissible evidence=To see if the evidence is good enough the investigator must approve it and once the evidence is in the court the judge must approve it.
Inadmissible evidence = Hearsay- that is when you heard that someone else said that someone did something
-This was not taken under oath
-This cannot be cross-examined
-This is not admissible evidence in a criminal case
-This IS admissible in civil cases- (for ex: divorce, household)
Evidence:
History- in china they used fingerprints as a signature
Henry Fauld- found ridge patterns on the fingers
This is a method that they can use to identify criminals
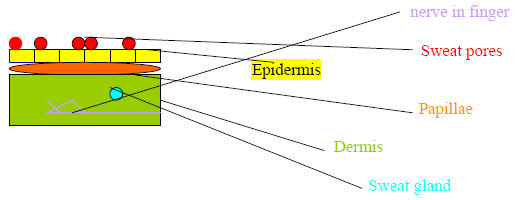
Fingerprints:
Characteristics:
1-general
a-Loop- 60-65 % of population has this type
b- Whorl- 30-35% of population has this type
c- Arch- 5% of population has this type
2- Specific
a- bifurcation- there is a split in the ridge
b-enclosure- it has a split but then it comes back together at the end of the ridge
c- short ridge- a regular ridge that does not continue all the way down the finger
d- island- a ridge that is not a line it is just there
e- delta - an upward "v" shape
f- cross over- the ridges cross over each other
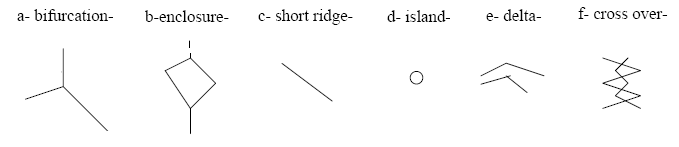
Classification = AFIS this is how they classified the fingerprints so they were able to find them easily until they got computers.
How are fingerprints detected?
Three different type of fingerprints:
1- Visible prints: can be seen with out aides.
Ex: blood print, grease print, ink print.
2- Plastic prints: prints found in soft materials
Ex: putty, wax, soap, and dust
Putty = art, construction, repair materials.
This one may or may not need an aide to see the print
3-invisible print: these types of prints are left by oils or perspiration (sweat)
Left on hard non-absorbent materials for ex:
-Mirror, glass, tile, painted wood.
Powder treatment-
1- Gray powder: made of aluminum and contains aluminum dust.
This is used on dark surfaces. And on mirrors and polished surfaces
- you use this by: applying powder to the print that you can not see and when you take the picture you are then able to see the print from the powder in the picture.
2- Black Powder- contains carbon or charcoal-
Used on light surfaces-
Use a fiberglass or camel hairbrush to apply the powder and you must apply the powder very carefully.
3- Magnetic sensitive powder: spread with magma brush.
Non-bristle brush- comes in two colors- black and gray-
Used on finish leather and rough plastics
4- Florescent light method: they use UV light that will cause the powder to Flores (cause it to be seen)
To take prints you must:
Put on powder
Place tape on top
Carefully lift the tape
And place onto index card- that way the print will last a long time.
SOFT AND POROUS SURFACES- paper, cardboard, cloth
-Iodine fuming: a substance that turns solid to gas (sublimation)(with out going through liquid state)
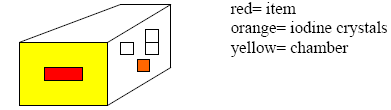
1 takes the item you want prints from and place it in the chamber
2 put iodine crystals into chamber
3 heat it
4 the iodine will convert from solid from to gas from
5 then you have your fingerprints because the gas shows the prints.

Return to Junior Review Sheets
Review Sheets Central
www.reviewsheetscentral.com